- What is Burns?
- Key Facts about Burns
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Step-by-Step Guidance / First Aid Procedures
- First Aid for Burns
- Trainer Tips / Safety Advice
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Conclusion / Summary
Burns: Essential First Aid Glossary
What is Burns?
Burns are injuries to the skin or other tissues resulting from heat, chemicals, electricity, sunlight, or radiation. They are classified according to their severity, which can significantly affect treatment options and healing times.
—
Key Facts about Burns
Causes
– Thermal Burns: Caused by contact with hot liquids (scalds), flames, steam, or hot objects.
– Chemical Burns: Result from exposure to caustic substances such as acids or alkalis.
– Electrical Burns: Occur due to electrical currents passing through the body.
– Radiation Burns: Often caused by prolonged exposure to the sun (sunburn) or radiation treatments.
Symptoms
– First-Degree Burns: Redness, minor swelling, and pain (e.g., sunburn).
– Second-Degree Burns: Blisters, swelling, and increased pain; skin may appear wet.
– Third-Degree Burns: White or charred skin, severe damage to deeper tissues; often painless due to nerve endings being destroyed.
Step-by-Step Guidance / First Aid Procedures
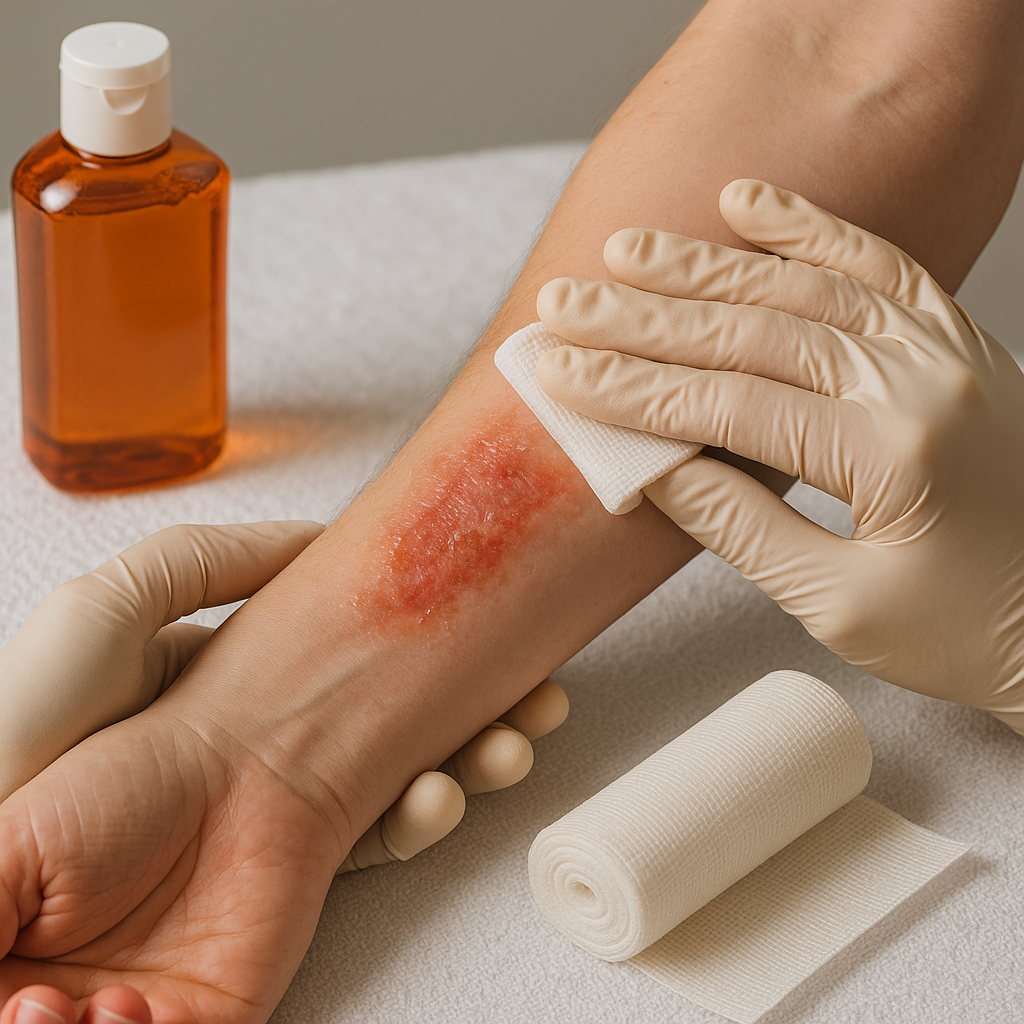
First Aid for Burns
1. Assess the Severity:
– First-Degree: Minor burns treated at home.
– Second-Degree: May require professional medical treatment.
– Third-Degree: Seek emergency assistance immediately.
2. Stop the Burning Process:
– Remove the source of the burn (if safe to do so). For chemical burns, flush the area with running water for at least 20 minutes.
3. Cool the Burn:
– Gently run cool (not cold) water over the burn for 10-20 minutes. Avoid ice, as it can further damage tissue.
4. Cover the Burn:
– Use a non-stick, sterile dressing to cover the burn lightly. Do not apply any creams, ointments, or ice directly to the wound.
5. Pain Management:
– For mild pain, consider over-the-counter pain relief medications according to age-appropriate guidelines.
6. Do Not Burst Blisters:
– If blisters form, they protect the underlying skin. Breaking them can lead to infection.
7. Seek Medical Attention:
– Call triple zero (000) for ambulances if:
– The burn is larger than the affected person’s hand.
– It is on the face, hands, feet, groin, or major joints.
– It is a chemical or electrical burn.
– The person is showing signs of shock (confusion, dizziness).
Trainer Tips / Safety Advice
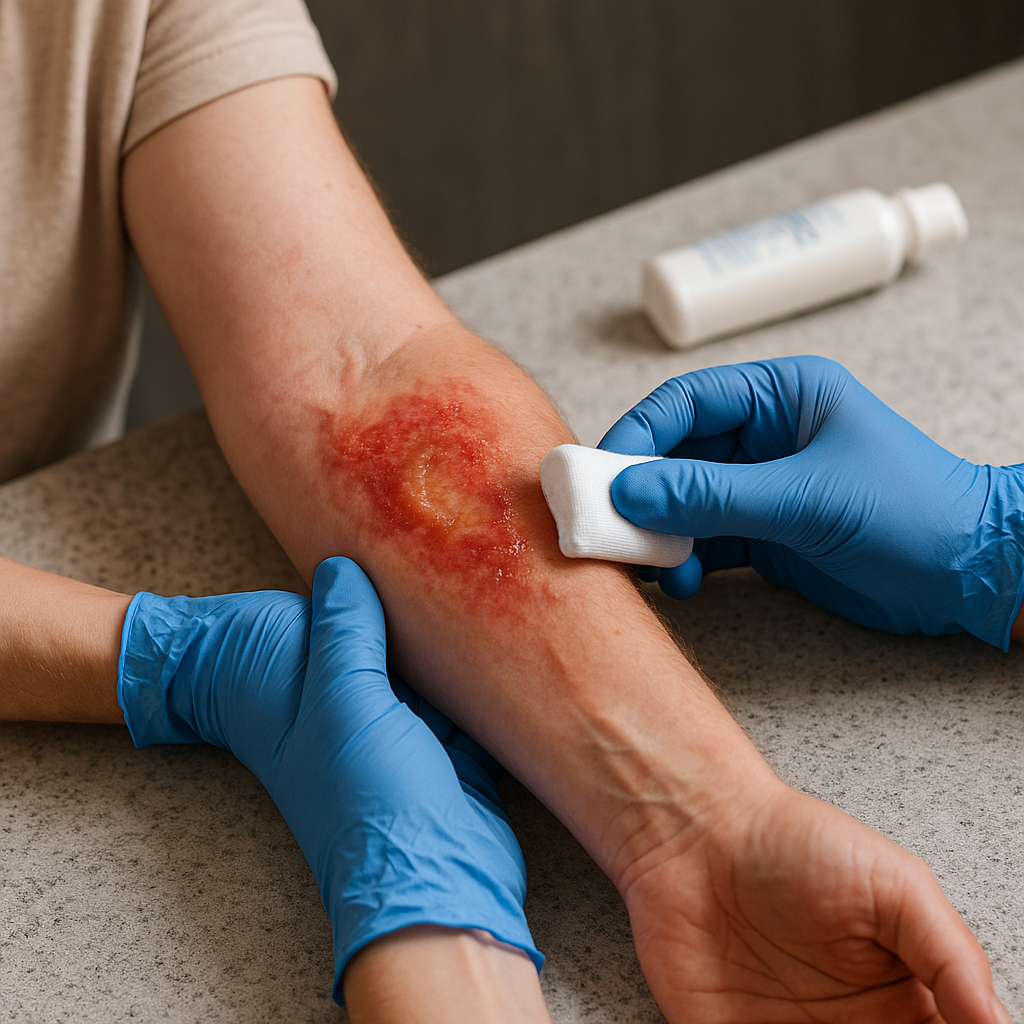
– Always Call for Help: When in doubt about the severity of a burn, especially with children or if chemical agents are involved, seek professional help.
– Avoid Home Remedies: Do not apply ice, butter, or any other unverified home remedies to burns as they can worsen the injury.
– Be Cautious with Children: Always ensure hot liquids and dangerous substances are out of reach.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
– Not Cooling the Burn Immediately: Prompt cooling can significantly reduce the severity of the burn.
– Ignoring Infection Signs: Watch for increasing redness, swelling, discharge, or fever.
– Using Adhesive Bandages: Always use sterile, non-stick dressings for burns to avoid sticking to the affected area.
Conclusion / Summary
Understanding the basics of burns and their first aid treatment is crucial for safety at home, work, and play. Remember, burns can escalate quickly if improperly treated. Always ensure to call emergency medical services for severe burns and follow the outlined first aid steps for minor injuries. Being equipped with burning knowledge can make a critical difference in ensuring effective care and recovery. Stay safe, informed, and proactive!
—
This comprehensive guide serves as a first aid glossary on burns. By following the outlined procedures and tips, you can help minimize the impact of burn injuries and ensure the best possible outcomes for those affected.

Leave a Reply